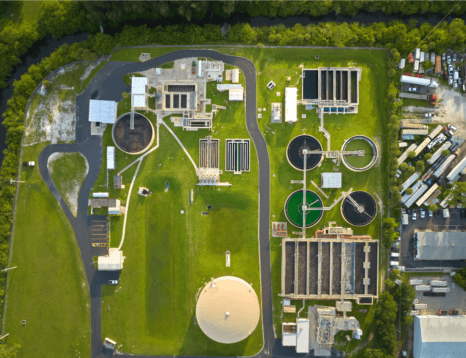
Sewage Treatment Plant STP in Bangladesh
Sewage Treatment Plant STP in Bangladesh are not just a solution to managing wastewater, these are a key driver of sustainable development. As Bangladesh experiences rapid urbanization and population growth, the need for effective sewage treatment becomes paramount. STPs, with advanced technologies like the Activated Sludge Process, Removal of hazardous contaminants, and advanced filtration systems, are at the forefront of this battle. They not only mitigate environmental pollution but also promote public health, making them a crucial component of Bangladesh's sustainable development strategy.
In Bangladesh, major cities like Dhaka, Chittagong, and Khulna have been prioritized in establishing STPs to manage wastewater. The public project plants, often managed by government agencies like the Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE) or municipal corporations, are a testament to the country's commitment to wastewater management. However, the potential for improvement lies in encouraging private sector involvement in building and operating STPs. This could significantly enhance efficiency and coverage, ensuring a more comprehensive approach to wastewater management in Bangladesh.
However, despite these efforts, there are still challenges in ensuring comprehensive sewage treatment coverage, especially in peri-urban and rural areas. Factors like inadequate infrastructure, limited financial resources, and lack of awareness contribute to the persistence of untreated sewage discharge, posing significant environmental and health risks. To address these challenges, ongoing investments in sewage treatment infrastructure, coupled with community engagement and regulatory measures, are essential to improve wastewater management in Bangladesh.
What is
Sewage Treatment used for?
Sewage treatment serves several important purposes:
- Public Health Protection: The primary purpose is to protect public health and the environment by removing harmful contaminants and pathogens from wastewater before it is discharged back into natural water bodies or reused.
- Water Pollution Prevention: Sewage treatment helps to prevent water pollution by removing pollutants such as organic matter, nutrients (like nitrogen and phosphorus), heavy metals, and pathogens that can harm aquatic ecosystems and human health.
- Resource Recovery: It allows for the recovery of valuable resources from wastewater, such as energy (through processes like anaerobic digestion or biogas production), nutrients (for reuse as fertilizer), and water (through various treatment processes for reuse in irrigation or industrial processes).
- Compliance with Regulations: Many countries have regulations and standards governing the treatment and discharge of wastewater to protect human health and the environment. Sewage treatment ensures compliance with these regulations.
- Reclamation and Reuse: Treated wastewater can be reclaimed and reused for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, industrial processes, and groundwater recharge, reducing the demand for freshwater resources.
Overall, sewage treatment plays a crucial role in maintaining public health, protecting the environment, and ensuring sustainable water management practices. By understanding the importance of this process, we can all contribute to a healthier and cleaner Bangladesh.
Types of
Sewage Treatment Plant in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) vary in type and scale, catering to the diverse needs of different regions. Some common types of sewage treatment plants found in Bangladesh include:
- Activated Sludge Process:This is one of the most widely used methods for treating sewage. It involves aerating sewage in aeration tanks where microorganisms break down organic matter. The activated sludge process is commonly used in larger cities and municipalities.
- Extended Aeration System:Similar to the activated sludge process, the extended aeration system provides longer aeration times, allowing for more thorough treatment of sewage. It's often employed in smaller towns and communities.
- Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR):SBR systems treat sewage in batches, where different stages of treatment (aeration, settling, and decanting) occur sequentially in the same tank. SBRs are known for their efficiency and flexibility and are suitable for areas with fluctuating sewage loads.
- Oxidation Ponds:Also known as stabilization ponds, oxidation ponds treat sewage through natural processes such as sunlight exposure and microbial action. They are cost-effective and are commonly used in rural areas and small communities.
- Constructed Wetlands:These systems use natural processes, including wetland vegetation and microbial action, to treat sewage. Constructed wetlands are environmentally friendly and are often used in decentralized settings or to treat wastewater from specific sources like industries or institutions.
- Septic Tanks:In rural and peri-urban areas where centralized sewage treatment is not feasible, individual or communal septic tanks are used. These tanks separate solids from liquids, allowing anaerobic bacteria to partially break down organic matter before discharge into the soil.
- Decentralized or Package Plants:These are compact sewage treatment systems designed for small communities, industries, or institutions. They often combine various treatment processes like sedimentation, biological treatment, and disinfection in a single unit.
These are just a few examples, and the choice of sewage treatment plant type depends on factors such as population density, available land, budget, and environmental regulations. It's important to be aware of these options as they can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of wastewater management in Bangladesh. Additionally, newer technologies and innovations may also be adopted to address specific challenges or improve treatment efficiency in Bangladesh.
Sewage Treatment Plant
STP and their Maintenance
STP Sewage treatment plants are crucial for managing wastewater, ensuring it's properly treated before being released back into the environment. Here's an overview of STPs and their maintenance:
- Primary Treatment: This is the first stage where solid waste is separated from liquid waste. Maintenance here involves regularly removing accumulated solids from sedimentation tanks and screens to prevent clogging.
- Secondary Treatment: In this stage, biological processes break down organic matter in the wastewater. Maintenance includes monitoring oxygen levels, pH, and temperature to ensure optimal conditions for microbial activity. Regular cleaning and inspection of aeration tanks, clarifiers, and biological filters are essential.
- Tertiary Treatment: This stage removes remaining contaminants such as nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus), pathogens, and fine solids. Maintenance involves monitoring chemical dosing systems, filters, and disinfection units to ensure effective treatment.
- Sludge Treatment: Sludge produced during the treatment process needs proper management. Regular removal and treatment of sludge prevent odors, minimize environmental impact, and allow for safe disposal or reuse.
- Instrumentation and Control Systems: STPs rely on various sensors and control systems to monitor and regulate treatment processes. Maintenance involves calibrating sensors, testing control systems, and updating software to ensure accurate data collection and efficient operation.
- Pumping Stations: Many STPs have pumping stations to transport wastewater. Maintenance includes inspecting pumps, valves, and motors for signs of wear or malfunction and ensuring proper lubrication and alignment.
- Safety and Environmental Compliance: Regular inspections and maintenance are necessary to comply with safety regulations and environmental standards. This includes maintaining emergency response equipment, containment systems, and conducting regular audits to identify and address potential hazards.
- Training and Staffing: Properly trained staff is essential for the efficient operation and maintenance of STPs. Regular training sessions ensure staff are knowledgeable about safety procedures, equipment operation, and emergency protocols.
- Record-Keeping and Documentation: Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities, equipment performance, and regulatory compliance is crucial for effective management and troubleshooting.
Overall, proactive maintenance is key to the reliable and efficient operation of sewage treatment plants, ensuring they continue to protect public health and the environment.
STP Requirements for
Residential Building in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, the requirements for residential building construction typically involve compliance with various regulations and standards set forth by the relevant authorities. While specific regulations may vary depending on the location and the type of residential building, here are some common aspects related to sewage treatment plant STP that might be required:
- Building Codes & Regulations: Residential buildings in Bangladesh must comply with national or local building codes and regulations such as the Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC). These codes often include requirements for sanitation and waste management systems, including STPs.
- Environmental Regulations: Environmental regulations may mandate the installation of STPs to ensure that residential wastewater is treated before being discharged into the environment. These regulations aim to protect public health and the environment from pollution.
- Local Government Requirements: Local municipalities or city corporations may have their specific requirements regarding STPs for residential buildings. These requirements may vary depending on the location and the size of the building.
- Design & Capacity: The design and capacity of the STP should be appropriate for the size and occupancy of the residential building. Factors such as the number of units, water usage patterns, and space availability will influence the design and capacity requirements.
- Effluent Standards: STPs must meet effluent standards set by the government or environmental agencies. These standards specify the acceptable levels of pollutants in the treated wastewater before it can be discharged into water bodies or reused for non-potable purposes.
- Maintenance & Operation: There may be requirements for regular maintenance and operation of the STP in building to ensure its proper functioning. Building owners or managers are typically responsible for ensuring that the STP is well-maintained and operated according to the regulations.
- Approval & Permits: Before installing an STP in a residential building, approval and permits from the relevant authorities may be required. This process often involves submitting design plans, environmental impact assessments, and other necessary documents for review and approval.
- Certification: After installation, the STP may need to be certified by qualified inspectors to ensure that it meets the required standards and regulations.
Developers, builders, and homeowners need to consult with local authorities and professionals specializing in wastewater management to ensure compliance with all applicable STP requirements for residential buildings in Bangladesh.
STP Requirements for
Factory in Bangladesh
Sewage treatment plant (STP) requirements for factories in Bangladesh are essential for several reasons:
§ Environmental Regulations: Bangladesh, like many other countries, has regulations in place to protect the environment. Factories are required to comply with these regulations to ensure that their operations do not adversely affect the surrounding environment, including water bodies.
§ Water Pollution Control: Industrial effluents can contain harmful pollutants that can contaminate water bodies if not treated properly. STP in factory helps in treating sewage and industrial wastewater before discharging it into water bodies, thereby reducing water pollution.
§ Public Health: Untreated sewage and industrial wastewater can pose serious health risks to the public. By treating wastewater before disposal, STPs help mitigate these risks by removing harmful pathogens and chemicals.
§ Sustainable Development: STPs play a crucial role in promoting sustainable development by conserving water resources and reducing pollution. Proper treatment of wastewater allows for its safe reuse in irrigation or other non-potable applications, thus reducing the strain on freshwater sources.
§ International Standards: With globalization, many factories in Bangladesh cater to international markets. Compliance with international environmental standards, which often require proper wastewater treatment, is essential for maintaining market access and reputation.
Overall, the implementation of STP requirements for factories in Bangladesh is crucial for protecting the environment, public health, and ensuring sustainable industrial development.
What measures are being taken to
encourage the private sector involvement in building and operating STPs in Bangladesh?
In Bangladesh, several measures are being taken to encourage private sector involvement in building and operating Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs). These measures aim to address the growing challenges of urbanization, pollution, and sanitation. Some of the key strategies include:
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): The government has been promoting PPPs to leverage private sector expertise and investment in developing and operating STPs. PPPs involve collaboration between the government and private entities to share risks, responsibilities, and benefits.
- Policy Support and Incentives: The government has been providing policy support and incentives to attract private sector participation. This includes offering tax incentives, land allocation, streamlined approval processes, and regulatory support to facilitate private investment in STPs.
- Transparent Bidding Processes: Transparent and competitive bidding processes are being implemented to ensure fair opportunities for private sector participation. This encourages private companies to compete for STP projects based on their technical expertise, efficiency, and financial viability.
- Capacity Building and Technical Assistance: Capacity building programs and technical assistance are provided to help local private companies enhance their capabilities in designing, building, and operating STPs. This includes workshops, training programs, and knowledge-sharing initiatives.
- Risk Mitigation Measures: The government may provide guarantees or risk-sharing mechanisms to mitigate financial risks for private investors involved in STP projects. This helps to improve the attractiveness of investment in the sector.
- Tariff Mechanisms: Clear and sustainable tariff mechanisms are established to ensure that private sector investments in STPs are financially viable. This involves setting reasonable tariffs for sewage treatment services while ensuring affordability for users.
- Regulatory Framework: A robust regulatory framework is in place to oversee the performance of private sector-operated STPs and to ensure compliance with environmental standards and regulations.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in the planning and implementation of STP projects helps to build trust and support for private sector involvement. Community involvement can also enhance the sustainability and social acceptance of STP initiatives.
By implementing these measures, Bangladesh aims to harness the efficiency, innovation, and investment potential of the private sector to address the critical need for sewage treatment infrastructure and improve environmental sustainability.
What are some of the challenges faced in
ensuring comprehensive sewage treatment coverage in Bangladesh's peri-urban and rural areas, and how are they being addressed?
Ensuring comprehensive sewage treatment coverage in peri-urban and rural areas of Bangladesh poses several challenges, including:
- Lack of Infrastructure: Many peri-urban and rural areas lack the necessary infrastructure for sewage treatment, including sewage collection networks and treatment plants.
- Limited Resources: Limited financial and human resources hinder the establishment and maintenance of sewage treatment facilities in these areas.
- Population Growth: Rapid population growth in peri-urban areas strains existing sewage systems and makes it challenging to provide adequate coverage.
- Awareness and Behavior Change: Lack of awareness about the importance of proper sewage treatment and hygiene practices can lead to improper disposal of sewage, exacerbating pollution and health risks.
- Geographical Factors: Some rural areas may have geographical challenges such as low-lying terrain or high groundwater levels, making traditional sewage treatment methods less effective.
To address these challenges, various strategies are being implemented:
- Community Engagement and Awareness: Initiatives to raise awareness about the importance of proper sewage treatment and hygiene practices are being undertaken. These include community education programs and campaigns to promote behavior change.
- Decentralized Treatment Systems: Implementing decentralized sewage treatment systems, such as septic tanks and constructed wetlands, can be more feasible and cost-effective in rural and peri-urban areas compared to centralized treatment plants. These systems can be tailored to suit local conditions and require less infrastructure.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Engaging the private sector in the provision of sewage treatment services can help leverage resources and expertise. PPPs can facilitate the construction, operation, and maintenance of sewage treatment infrastructure in peri-urban and rural areas.
- Government Initiatives and Policies: Government initiatives aimed at improving sanitation and wastewater management, such as the National Sanitation Strategy, focus on extending sewage treatment coverage to underserved areas. Policies and regulations are being developed and enforced to ensure compliance with sewage treatment standards.
- Technology Adoption: Innovative technologies for decentralized sewage treatment, such as modular treatment units and bio-digesters, are being explored to provide cost-effective solutions for peri-urban and rural areas.
By addressing these challenges through a combination of community engagement, infrastructure development, policy interventions, and technological innovations, efforts are being made to improve sewage treatment coverage in Bangladesh's peri-urban and rural areas.
Are there any new and innovative
sewage treatment technologies being developed or implemented in Bangladesh, and if so, what are they?
Bangladesh has been exploring various sewage treatment technologies to address its growing sanitation challenges. Here are a few notable innovations:
- Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS): DEWATS are gaining popularity in Bangladesh as they offer cost-effective and efficient solutions for treating sewage in decentralized settings, such as communities or individual households. These systems utilize natural processes like anaerobic digestion, aerobic treatment, and filtration to purify wastewater.
- Constructed Wetlands: Constructed wetlands mimic natural wetland ecosystems to treat wastewater. In Bangladesh, these wetlands are being constructed to treat sewage from small communities or industrial sources. They are relatively low-cost and environmentally friendly, providing an effective means of wastewater treatment.
- Biogas Plants: Some sewage treatment facilities in Bangladesh incorporate biogas production as a byproduct of the treatment process. Biogas can be utilized for cooking, lighting, or generating electricity, providing an additional incentive for wastewater treatment while also addressing energy needs.
- Filtration Technologies: Advanced filtration technologies, such as membrane bioreactors (MBRs) and reverse osmosis (RO), are being explored for treating sewage in urban areas where space is limited. These technologies offer high levels of purification and are particularly suitable for producing reclaimed water for non-potable uses.
- Solar-Powered Treatment Systems: Given Bangladesh's abundant sunlight, solar-powered sewage treatment systems are being developed and implemented in rural areas where access to electricity is limited. These systems utilize solar energy to power treatment processes, making them sustainable and cost-effective solutions for remote communities.
- Resource Recovery from Wastewater: Efforts are being made to recover valuable resources from wastewater, such as nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as organic matter for use as fertilizers or energy sources. Innovative technologies like nutrient recovery systems and anaerobic digestion are being integrated into sewage treatment plants to extract these resources.
These technologies represent a diverse range of approaches aimed at improving sewage treatment in Bangladesh, addressing both environmental and socio-economic challenges associated with inadequate sanitation infrastructure. Ongoing research and innovation in this field are essential for achieving sustainable wastewater management in the country.
Why Should You Choose
Kingsley Engineering Service Corporation for Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)?
In the quest for effective sewage management in Bangladesh, we, Kingsley Engineering Service Corporation, stand unrivaled, offering unmatched expertise and innovative solutions that set the standard for the sewage treatment industry. Here's why we are the undisputed leader in sewage treatment across the country:
- Proven Track Record: With a portfolio boasting successful STP projects, we have demonstrated our ability to deliver results consistently. These projects, executed with precision and efficiency, serve as shining examples of our expertise in the field. Our remarkable achievements lie in our successful execution of various Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) projects across Bangladesh. Projects like,
- Bijoy Rakeen City [Capacity: 320 m3/day, Treatment technology -Biological Oxidization with filling materials]
- Independent University of Bangladesh, IUB [Capacity: 250 m3/day, Treatment technology-AAO process with Bio-filling materials ]
- BGMEA Complex [capacity: 125 m3/day, Treatment technology - Membrane Bio-Reactor (MBR) Technology]
- Cityscape Tower [capacity: 40 m3/day, Treatment technology - Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)]
We have demonstrated proficiency in implementing cutting-edge solutions tailored to each project's requirements.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: We are at the forefront of sewage treatment technology in Bangladesh, pioneering the adoption of advanced methods like MBR, MBBR, and AAO. By leveraging the latest innovations, we ensure optimal performance and environmental sustainability in every project.
- Comprehensive Services: Unlike other companies, we offer end-to-end solutions for sewage treatment such as EPC contract, process design, and calculation, covering design, construction, maintenance, and consultation. This holistic approach streamlines the project lifecycle, delivering seamless execution and long-term efficiency.
- Environmental Sustainability: Our commitment to sustainability is unparalleled. By offering packaged STPs with recycle and reuse options, we minimize environmental impact while maximizing resource utilization. This eco-conscious approach resonates with clients seeking sustainable solutions.
- Lowest Maintenance Costs: Our STPs are not only technologically advanced but also cost-effective. With minimal maintenance requirements and optimized chemical usage, we offer the lowest maintenance costs in the market, ensuring long-term affordability for clients.
- Expert Team: Kingsley has a team of elite engineers and technicians, renowned for their expertise and dedication. With 24/7 support and personalized service, we ensure that clients receive the highest level of assistance at every stage of the project.
In essence, Kingsley Group's unparalleled combination of expertise, technology, comprehensive services, sustainability, affordability, and elite team make it the ideal choice for sewage treatment projects in Bangladesh. As our country strives for a cleaner and healthier future, Kingsley remains the undisputed leader, driving innovation and setting new standards in sewage treatment excellence.
Technology for a
Sustainable Future
Kingsley™ focuses on long term & sustainable future with a reliable technology.