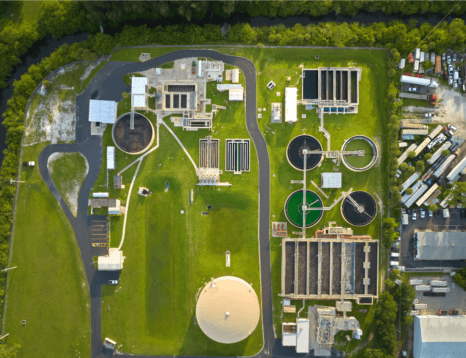
What is Effluent Treatment Plant?
Effluent treatment plant (ETP) helps treat the wastewater or effluent that is produced by different industrial operations before it is released or discharged into the environment or used again. The primary objective of an ETP is to remove contaminants and pollutants from the wastewater to make it safe for disposal or to minimize its impact on the environment.
Key components of an Effluent Treatment Plant typically include:
- Pretreatment: This involves screening and removing large solids, debris, and oil/grease from the wastewater to prevent damage to downstream treatment equipment.
- Primary Treatment: In this stage, physical processes, for example, flotation or sedimentation, are used to separate suspended solids and organic matter from the wastewater.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological processes such as activated sludge process, biological filters, or constructed wetlands are employed to further degrade organic pollutants and nutrients present in the wastewater.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced treatment methods such as filtration, chemical precipitation, or membrane processes may be utilized to remove remaining contaminants to meet specific discharge standards or for water reuse purposes.
- Sludge Handling: Sludge generated during the treatment process is typically treated separately to reduce its volume and stabilize it for safe disposal or reuse.
Effluent Treatment Plants are essential for industries to comply with environmental regulations and minimize their impact on surrounding ecosystems and public health. The design and operation of an ETP depend on factors such as the type and volume of wastewater generated, the specific contaminants present, and local discharge regulations.
Features and Benefits of Effluent Treatment Plant
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) play a crucial role in treating industrial wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. Here are some of the key features and benefits of Effluent Treatment Plants:
Features of
Effluent Treatment Plant:
- Physical, Chemical, and Biological Treatment: ETPs employ various processes such as sedimentation, filtration, chemical treatment (like coagulation, flocculation), and biological treatment (like activated sludge process, aerobic and anaerobic digestion) to remove pollutants from wastewater.
- Customization: ETPs can be customized based on the specific requirements of different industries and the nature of pollutants present in their wastewater.
- Monitoring and Control Systems: Modern ETPs often include advanced monitoring and control systems to ensure efficient operation and compliance with regulatory standards. These systems may include sensors, meters e.g. Electro-Magnetic Flowmeter (EMF), and automated controls.
- Sludge Management: ETPs also handle the management of sludge generated during the treatment process, including dewatering, drying, incineration and disposal or reuse.
- Safety Measures: Safety features such as emergency shutdown systems, alarms, and protective barriers are often incorporated into ETP designs to mitigate risks associated with handling potentially hazardous chemicals and processes.
Benefits of
Effluent Treatment Plant:
- Environmental Protection: One of the primary benefits of ETPs is their ability to remove harmful pollutants from wastewater, thus preventing contamination of natural water bodies and safeguarding the environment.
- Compliance with Regulations: ETPs help industries comply with environmental regulations and standards set by regulatory authorities regarding wastewater discharge limits for various pollutants.
- Resource Conservation: ETPs enable the recycling and reuse of water, thereby conserving freshwater resources and reducing the strain on natural water sources.
- Public Health: By treating wastewater before discharge, ETPs help protect public health by reducing the risk of waterborne diseases and contamination of drinking water sources.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Investing in ETPs demonstrates a company's commitment to environmental sustainability and corporate social responsibility, enhancing its reputation among stakeholders and the community.
- Cost Savings: While initial investment in ETPs may be significant, they often lead to long-term cost savings for industries through reduced water consumption, lower disposal costs, and potential revenue generation from by-products or recycled water.
- Operational Efficiency: Properly functioning ETPs improve the overall efficiency of industrial processes by ensuring the availability of clean water for various manufacturing activities and reducing downtime due to regulatory non-compliance or environmental incidents.
Overall, Effluent Treatment Plants offer a range of features and benefits that are essential for both environmental protection and the sustainable operation of industries.
Necessity of Effluent Treatment Plant
in Bangladesh
The necessity of an Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) in Bangladesh is paramount due to several factors:
- Environmental Protection: Bangladesh faces significant environmental challenges due to industrial pollution, especially in sectors like textiles, Chemical, food and pharmaceuticals. Without proper treatment, effluents from these industries can contaminate water bodies, soil, and air, leading to severe ecological damage.
- Health Concerns: Untreated industrial effluents contain various toxic chemicals and heavy metals, posing serious health risks to both humans and wildlife. These pollutants can enter the food chain and accumulate in organisms, leading to long-term health problems.
- Legal Compliance: Bangladesh has environmental regulations in place that mandate industries to treat their effluents before discharge. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal actions, and even closure of non-compliant facilities.
- International Trade: With increasing globalization, adherence to environmental standards is crucial for international trade. Many export-oriented industries in Bangladesh must meet the environmental requirements of their trading partners, which often include treating their effluents to acceptable levels before disposal.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Bangladesh, like many other countries, has committed to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals set by the United Nations. Proper management of industrial effluents is essential for achieving goals related to clean water and sanitation (SDG 6), responsible consumption and production (SDG 12), and sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11).
- Community Welfare: Effluent treatment not only protects the environment and public health but also contributes to the overall well-being of communities living near industrial areas. Reduced pollution leads to cleaner air, water, and soil, enhancing the quality of life for residents.
- Employment Opportunities: The establishment and operation of ETPs create employment opportunities for skilled workers involved in designing, installing, operating, and maintaining these systems, contributing to economic development.
Effluent Treatment Plants are crucial for treating wastewater from these industries to meet regulatory standards and protect the environment and public health. Proper treatment helps remove or reduce the concentration of pollutants before they are discharged into water bodies or reused in industrial processes.
What industries in Bangladesh mostly require ETPs, and what are the specific pollutants in their wastewater?
In Bangladesh, several industries require Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) due to the nature of their operations and the pollutants they generate. Some of the key industries that typically require ETPs include:
- Textile and Garment Industry: Bangladesh has a significant textile and garment industry, which often generates wastewater containing pollutants such as dyes, pigments, chemicals used in dyeing and printing, as well as suspended solids and organic matter.
- Tannery or Leather Industry: The leather industry is another major sector in Bangladesh, and its wastewater can contain high levels of organic pollutants, chromium, sulfides, and other chemicals used in the tanning process.
- Pharmaceuticals Industry: Pharmaceuticals manufacturing generates wastewater containing various chemicals, including active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), solvents, and other contaminants.
- Food Processing Industry: Wastewater from food processing facilities can contain organic matter, fats, oils, grease, and nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Chemical Industry: Chemical manufacturing facilities produce wastewater containing a wide range of chemicals depending on their specific processes, including acids, alkalis, heavy metals, and organic compounds.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: This industry generates wastewater containing organic compounds from wood pulp processing, as well as chemicals used in bleaching and papermaking processes.
Specific pollutants found in the wastewater of these industries can include:
- Organic pollutants: Such as dyes, solvents, oils, fats, greases, organic chemicals, and other biological substances.
- Heavy metals: Including chromium, lead, cadmium, mercury, and others, often originating from industrial processes and chemical treatments.
- Suspended solids: Solid particles suspended in the wastewater, which can include both organic and inorganic matter.
- Nutrients: Nitrogen and phosphorus, which can contribute to eutrophication in water bodies if not properly treated.
- Acids and alkalis: These are from various industrial processes that can affect the pH of the wastewater and the receiving water bodies.
- Toxic chemicals: Depending on the specific processes involved in each industry, various toxic substances may be present in the wastewater, posing risks to the environment and public health if discharged untreated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the establishment of Effluent Treatment Plant in Bangladesh is not only necessary but also crucial for sustainable development, environmental protection, public health, legal compliance, and international trade. It requires concerted efforts from both the government and industries to ensure effective implementation and enforcement of regulations regarding industrial wastewater treatment.
Technology for a
Sustainable Future
Kingsley™ focuses on long term & sustainable future with a reliable technology.